Saas software is distributed through the internet, either directly from the software vendor’s website or through third-party resellers. The software is accessed through a web browser or mobile application that connects to the internet, and does not require pre-installation on an operating system, a flash drive, or an optical disc.
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based software delivery model that has become increasingly popular in recent years. In the past, software had to be installed on a computer, but with SaaS, the software is accessed through the internet.
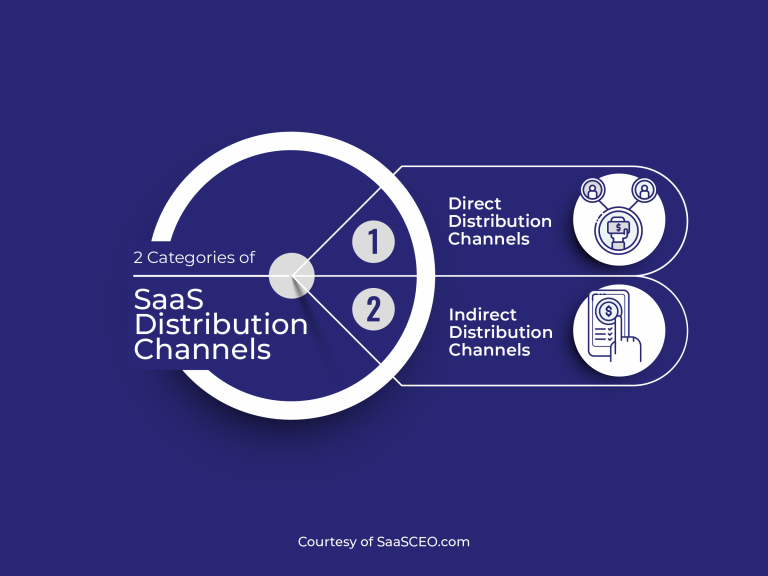
SaaS is typically distributed through a direct or indirect distribution model, with the software vendor selling products directly to customers or through third-party resellers. The software is accessed through a web browser or mobile application and does not require installation on an operating system, flash drive or optical disc. This model allows businesses to access software without having to manage the hardware infrastructure required to support it.
Direct Saas Distribution Model
In a direct SaaS distribution model, software vendors sell their products directly to customers through their website. On the other hand, in an indirect model, vendors distribute their products through third-party resellers who then sell them to customers. SaaS software is distributed through the internet and does not require pre-installation on an operating system, a flash drive, or an optical disc.
he direct SaaS distribution model involves the software vendor selling their products directly to customers through their website or another online platform, cutting out any middlemen. This can be an effective way for companies to maintain control of their product distribution and build a direct relationship with their customers. In this section, we’ll provide a definition, examples of companies that use this model, and a list of pros and cons to help you understand this model further.Definition And Explanation
The direct SaaS distribution model involves selling software directly to customers through the vendor’s website or another online platform, eliminating the need for intermediaries like resellers or distributors. In this model, the software vendor maintains control of the entire sales process, from marketing to payment and delivery. Customers can purchase and access the software directly from the vendor, creating a direct relationship between the software vendor and the customer.Examples Of Companies Using Direct Saas Distribution
There are many examples of companies that have built a successful business using the direct SaaS distribution model. Here are three:- Canva: An online graphic design platform that sells its subscription-based software directly to customers through its website.
- Slack: A collaboration software tool that offers free and paid plans to customers, sold directly through their website.
- Zoho: A suite of online productivity tools for businesses that are sold directly to customers through their website.
Pros And Cons
Like any distribution model, there are both advantages and disadvantages to using the direct SaaS distribution model. Here are some of the most significant pros and cons: Pros:- Control: The software vendor maintains control over the entire sales process, allowing for increased control over branding, pricing, and customer support.
- Direct Relationship: The vendor can build a direct relationship with its customers, leading to valuable customer insights, feedback, and loyalty.
- Higher Margins: Cutting out middlemen means that the vendor can often realize higher profit margins on each sale.
- Limited Reach: Without intermediaries, the vendor may have a harder time reaching a wider range of customers and expanding their market share.
- Sales Team: Without intermediaries to handle sales, the vendor may need to invest in building its own sales team to grow their customer base.
- Increased Costs: Building and maintaining their own sales platform can be costly, potentially eating into profits.
Credit: www.saasceo.com
Indirect Saas Distribution Model
In an indirect SaaS distribution model, third-party resellers distribute software products to customers, rather than a software vendor selling directly. This model allows for wider reach and increased sales, as resellers can leverage their established customer base and promote the software to potential customers.
Indirect SaaS Distribution Model In an indirect SaaS distribution model, software vendors distribute their products through third-party resellers who then sell them to customers. This is done through value-added resellers (VARs) or through affiliate marketing programs. In this model, the software vendor relies on the reseller to market their product and provide customer support. H3: Definition and explanation The indirect SaaS distribution model involves the distribution of software through third-party resellers. This model allows software vendors to expand their reach by leveraging the reseller’s network and expertise. H3: Examples of companies using indirect SaaS distribution Some examples of companies using the indirect SaaS distribution model include Salesforce, Microsoft, and Adobe. Salesforce uses a network of VARs and consultants to sell and support their products. Microsoft has an extensive channel network that includes VARs and system integrators. Adobe uses affiliate marketing programs to distribute their Creative Cloud suite of products. H3: Pros and cons Pros: – Larger reach: The indirect SaaS distribution model allows software vendors to expand their reach by leveraging the reseller’s network and expertise. – Cost-effective: Using a third-party reseller can be cost-effective for software vendors as they do not have to invest in building their own distribution and support infrastructure. – Increased customer satisfaction: The reseller provides customer support and can ensure customer satisfaction by addressing their specific needs. Cons: – Lack of control: Software vendors may have less control over the distribution process as they rely on the reseller to market and support their product. – Reduced margins: The reseller takes a cut of the revenue, reducing the margins for the software vendor. – Conflicting interests: The reseller may have interests that conflict with those of the software vendor, such as promoting competing products. In conclusion, the indirect SaaS distribution model is a way for software vendors to expand their reach and leverage the expertise of third-party resellers. While it has its pros and cons, it is a valuable distribution model that can benefit both software vendors and resellers alike.Saas Distribution Channels
O does not have technical knowledge? SaaS (Software as a Service) is a software delivery model where users access software over the internet. Instead of installing and maintaining software on their own computer, users can easily access the software from anywhere with an internet connection.
SaaS products typically offer upfront cost savings, automatic updates, and scalability.
SaaS software is widely distributed through the internet as it is a cloud-based software that can be accessed via a web browser or mobile application. There are two SaaS distribution models – direct and indirect. In a direct SaaS distribution model, the software vendor sells their product directly to customers. In contrast, in an indirect SaaS distribution model, the software vendor distributes its products through third-party resellers who then sell them to customers.Marketing And Networking Strategies
To effectively distribute SaaS software, marketing and networking strategies play a crucial role. Companies create a brand image and brand awareness through efficient marketing strategies like social media marketing, internet advertising, email marketing campaigns, and blog posts. Additionally, networking with industry influencers, customers, and potential affiliates will help promote software products to a targeted audience.Third-party Resellers
In the indirect SaaS distribution model, third-party resellers have a significant impact on the distribution of SaaS software. Software vendors often partner with resellers to increase their sales channels. Resellers help expand the product reach by promoting and selling software to their existing customer bases. The software vendors provide the reseller with marketing materials, training, and sales support to ensure that they have the required knowledge to close sales and achieve the set targets.Comparison Between Direct And Indirect Distribution Channels
In direct SaaS distribution, customers buy software directly from the vendor. There is no intermediary between the software vendor and the customer. This model offers the software vendor direct control over the product and customers’ feedback. On the other hand, the indirect SaaS distribution model involves third-party intermediaries like resellers who bridge the gap between the vendor and customers. The indirect model offers the software vendor a wide distribution network with increased sales potential but with less control over the product and customer feedback. To sum up, SaaS distribution channels play a vital role in the proliferation of software products to a targeted audience. Through effective marketing and networking strategies, coupled with reliable third-party resellers, software vendors can increase sales channels and reach new customers. The choice between direct and indirect distribution models depends on the software vendor’s preference, business objectives, and target market.Evolution Of Saas
In the world of software, SaaS (Software as a Service) has become a popular distribution model. Instead of pre-installation on an operating system or distribution through physical media, SaaS is accessible through the internet, making it more convenient for both software vendors and users.
The evolution of SaaS has brought about significant changes in the way software is distributed and delivered. Initially, Service-oriented architectures (SOA) emerged as a paradigm for distributed computing and enterprise integration. However, SOA faced several challenges such as data integrity and consistency management. As a result, Microservices architecture (MSA) emerged as a way to address these challenges and design software applications as suites of independently deployable services. MSA brought dynamism, modularity, and distributed development to the table. Service-oriented architectures (SOA)SOA is an architectural style that involves providing services to other components or applications and organizing them in a loosely coupled way to allow communication between various software systems. Software vendors like Salesforce.com and Netsuite specialize in SOA to deliver their services. However, SOA has several limitations that MSA has been designed to overcome. Microservices architecture (MSA)
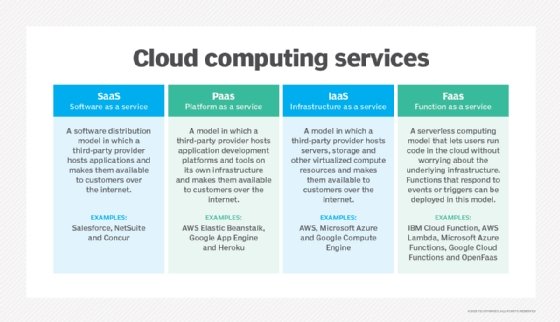
MSA represents an architectural approach to building software applications as a collection of small, independent services. Compared to the monolithic architecture, MSA is more flexible and scalable as it allows for faster updates and releases without affecting the entire system. It also enables easy scale-up or scale-down of individual services. Cloud computing, Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Cloud computing is a service delivery model where users can access software applications, data storage, and processing power over the internet. Software vendors and developers use cloud services like Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) to make their applications available to customers without the need for expensive hardware investments. PaaS offers software development tools, while IaaS provides virtual servers, storage, and networks. Overall, SaaS software distribution has evolved significantly over the years due to the changing needs of businesses and customers. By leveraging technology and the latest architectural approaches, software vendors are now able to deliver innovative solutions that are faster, more flexible, and scalable for their customers.
Examples Of Saas Software
Is not tech-savvy? SaaS software is distributed through the internet and accessed through a web browser or mobile application. The software is not pre-installed on an operating system, flash drive, or optical disc. In a direct distribution model, software vendors sell products directly to customers, while in an indirect distribution model, vendors distribute products through third-party resellers.
Examples of SaaS Software SaaS software is a popular way of delivering software solutions to customers. It is distributed through the internet, allowing customers access to the software via a web browser or mobile application. This cloud-based software can be accessed from anywhere, making it a popular choice for businesses worldwide. Popular Companies Offering SaaS Software Many large corporations offer SaaS software solutions to their customers. These solutions cover a vast range of applications, from project management to accounting and human resources. Here are some examples of the most popular companies that offer SaaS software solutions: 1. Salesforce: A cloud-based CRM tool for businesses of all sizes. 2. Dropbox: A file-sharing and collaboration tool used for cloud file storage. 3. Microsoft: Provides cloud-based Office 365 and customer relationship management solutions. 4. Google: Provides a range of cloud-based tools, including Gmail, Drive and Google Calendar. Types of SaaS Software SaaS software can be categorized based on its function, platform, and pricing model. Here are some of the most common types of SaaS software: 1. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software: SaaS software solutions that integrate various business processes, including accounting, inventory management, and human resources. 2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software: SaaS software solutions that help businesses manage their customer relationships. 3. Human Resource Management (HRM) software: SaaS software solutions that help organizations streamline employee management tasks, such as payroll and benefits administration. 4. Marketing Automation software: SaaS software solutions that help businesses automate marketing tasks, such as email campaigns and social media management. Classification of SaaS Software as Service or Product SaaS software can be classified as either a service or product. SaaS software that is sold directly to the customer is a service. The vendor sells the software through its website to the customer. In contrast, indirect SaaS distribution is classified as a product. The vendor distributes the software through third-party resellers who then sell it to customers. In conclusion, SaaS software is a popular way of distributing software solutions to businesses worldwide with examples of popular companies, types, and classifications.
Credit: www.saasceo.com
Credit: www.techtarget.com
Frequently Asked Questions For How Is Saas Software Distributed
How Is Saas Software Distribution?
SaaS software is distributed through direct or indirect models. In the direct model, the vendor sells directly to customers through its website. In the indirect model, the vendor distributes through third-party resellers. SaaS software is accessed through the internet and does not require physical installation such as optical discs or flash drives.
What Is The Saas Model Of Software Delivery?
SaaS (Software as a Service) is a cloud-based software delivery model where the software is accessed through the internet, without the need for installation on a computer or server. It is distributed directly to customers through a vendor’s website or indirectly through third-party resellers.
It is sold on a monthly subscription or annual fee basis, and users can access it through a web browser or mobile application.
How Do Saas Companies Work?
SaaS software is typically distributed through the internet. There are two models for distribution – direct and indirect. Direct SaaS distribution is where the vendor sells products directly to customers, while indirect distribution involves third-party resellers selling the products to customers.
SaaS software does not require pre-installation on an operating system, a flash drive, or an optical disc.
How Do Saas Applications Work?
SaaS software is typically distributed through the internet, accessed via a web browser or mobile application, eliminating the need for physical installation on an operating system. There are two common distribution models, direct and indirect. In the direct model, the vendor sells products directly to customers through their website.
In the indirect model, the vendor sells through third-party resellers. SaaS is software offered on a monthly or annual subscription basis and is owned by the vendor.
Conclusion
SaaS software distribution can be done in two ways: direct and indirect. A vendor can sell the products directly to customers through its website or distribute the products through third-party resellers. As a cloud-based software, SaaS is distributed through the internet and can be accessed via a web browser or mobile application.
The evolution of SaaS started with service-oriented architectures and moved to microservices architecture, forming SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Understanding SaaS distribution models is key to achieving business success.








Leave a Reply